100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

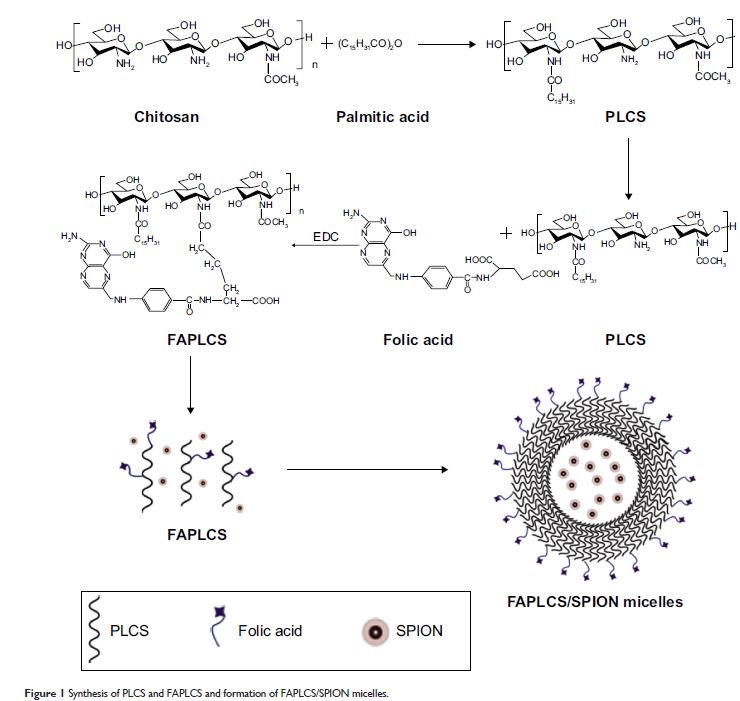
用于肿瘤靶向磁共振成像的高分子量壳聚糖聚合衍生物胶囊封装的超顺磁性氧化铁
Authors Xiao Y, Lin ZT, Chen Y, Wang H, Deng YL, Le DE, Bin J, Li M, Liao Y, Liu Y, Jiang GB, Bin J
Published Date February 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 1155—1172
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S70022
Received 28 June 2014, Accepted 12 October 2014, Published 5 February 2015
Abstract: Magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents based on chitosan derivatives have
great potential for diagnosing diseases. However, stable tumor-targeted MRI
contrast agents using micelles prepared from high molecular weight chitosan
derivatives are seldom reported. In this study, we developed a novel
tumor-targeted MRI vehicle via superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
(SPIONs) encapsulated in self-aggregating polymeric folate-conjugated
N-palmitoyl chitosan (FAPLCS) micelles. The tumor-targeting ability of
FAPLCS/SPIONs was demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. The results of dynamic
light scattering experiments showed that the micelles had a relatively narrow
size distribution (136.60±3.90 nm) and excellent stability. FAPLCS/SPIONs
showed low cytotoxicity and excellent biocompatibility in cellular toxicity
tests. Both in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that FAPLCS/SPIONs bound
specifically to folate receptor-positive HeLa cells, and that FAPLCS/SPIONs
accumulated predominantly in established HeLa-derived tumors in mice. The
signal intensities of T2-weighted images in established HeLa-derived
tumors were reduced dramatically after intravenous micelle administration. Our
study indicates that FAPLCS/SPION micelles can potentially serve as safe and
effective MRI contrast agents for detecting tumors that overexpress folate
receptors.
Keywords: superparamagnetic
iron oxide, magnetic resonance imaging, polymeric micelles, folate receptors,
tumor-targeted MRI, N-palmitoyl chitosan