100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

用于加强肿瘤细胞的凋亡的微乳液基协同双药物联合递送系统
Authors Qu D, Ma Y, Sun W, Chen Y, Zhou J, Liu C, Huang M
Published Date February 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 1173—1187
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S76742
Received 31 October 2014, Accepted 16 December 2014, Published 5 February 2015
Abstract: A
microemulsion-based synergistic dual-drug codelivery system was developed for
enhanced cell apoptosis by transporting coix seed oil and etoposide into A549
(human lung carcinoma) cells simultaneously. Results obtained by dynamic light
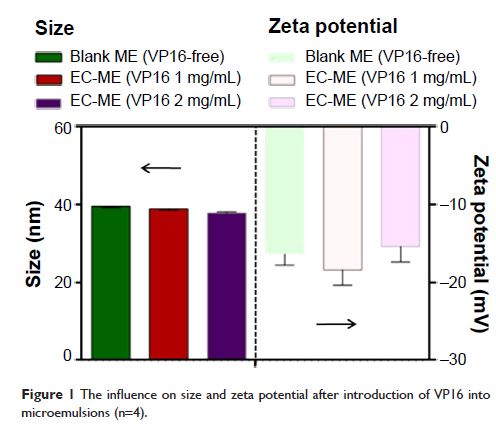
scattering showed that an etoposide (VP16)-loaded coix seed oil microemulsion
(EC-ME) delivery system had a small size around 35 nm, a narrow polydispersity
index, and a slightly negative surface charge. The encapsulating efficiency and
total drug loading rate were 97.01% and 45.48%, respectively, by
high-performance liquid chromatography. The release profiles at various pH
values showed an obvious pH-responsive difference, with the accumulated amount
of VP16 released at pH 4.5 (and pH 5.5) being 2.7-fold higher relative to that
at pH 7.4. Morphologic alteration (particle swelling) associated with a mildly
acidic pH environment was found on transmission electron microscopy. In the
cell study, the EC-ME system showed a significantly greater antiproliferative
effect toward A549 cells in comparison with free VP16 and the mixture of VP16
and coix seed oil. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration of the EC-ME
system was 3.9-fold and 10.4-fold lower relative to that of free VP16 and a
mixture of VP16 and coix seed oil, respectively. Moreover, fluorescein
isothiocyanate and VP16 (the green fluorescent probe and entrapped drug,
respectively) were efficiently internalized into the cells by means of coix seed
oil microemulsion through intuitive observation and quantitative measurement.
Importantly, an EC-ME system containing 20 µg/mL of VP16 showed a 3.3-fold and
3.5-fold improvement in induction of cell apoptosis compared with the
VP-16-loaded microemulsion and free VP16, respectively. The EC-ME combination
strategy holds promise as an efficient drug delivery system for induction of
apoptosis and treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: microemulsion,
synergistic effect, dual-drug codelivery, coix seed oil, apoptosis induction