100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

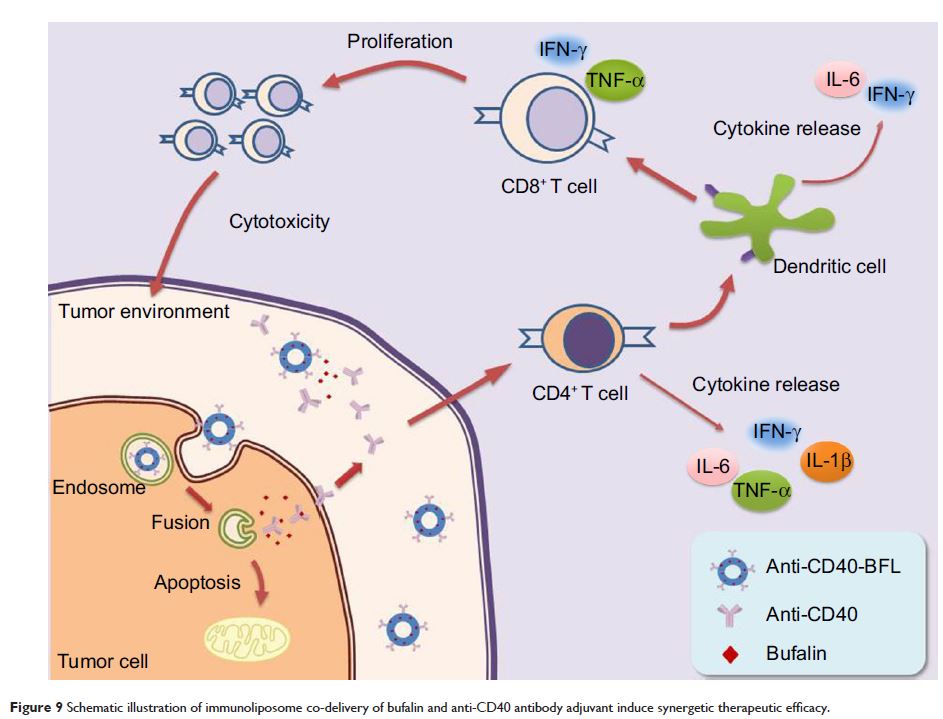
蟾毒灵与抗 CD40 抗体的免疫脂质体佐药共同给药带来对黑素瘤的协同疗效
Authors Li Y, Yuan J, Yang Q, Cao W, Zhou X, Xie Y, Tu H, Zhang Y, Wang S
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 5683—5700
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S73651
Received 2 September 2014, Accepted 25 October 2014, Published 4 December 2014
Abstract: Liposomes
constitute one of the most popular nanocarriers for improving the delivery and
efficacy of agents in cancer patients. The purpose of this study was to design
and evaluate immunoliposome co-delivery of bufalin and anti-CD40 to induce
synergetic therapeutic efficacy while eliminating systemic side effects.
Bufalin liposomes (BFL) conjugated with anti-CD40 antibody (anti-CD40-BFL)
showed enhanced cytotoxicity compared with bufalin alone. In a mouse B16
melanoma model, intravenous injection of anti-CD40-BFL achieved smaller tumor
volume than did treatment with BFL (average: 117 mm3 versus 270 mm3,
respectively); the enhanced therapeutic efficacy through a caspase-dependent
pathway induced apoptosis, which was confirmed using terminal deoxynucleotidyl
transferase-mediated dUTP-Fluorescein nick end labeling and Western blot assay.
Meanwhile, anti-CD40-BFL elicited unapparent body-weight changes and a
significant reduction in serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β,
interleukin-6, interferon-γ, and hepatic enzyme alanine transaminase,
suggesting minimized systemic side effects. This may be attributed to the
mechanism by which liposomes are retained within the tumor site for an extended
period of time, which is supported by the following biodistribution and flow
cytometric analyses. Taken together, the results demonstrated a highly
promising strategy for liposomal vehicle transport of anti-CD40 plus bufalin
that can be used to enhance antitumor effects via synergetic systemic immunity
while blocking systemic toxicity.
Keywords: liposomes, bufalin,
anti-CD40, chemoimmunotherapy