100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

顺利获得沉默 NEDD9 对胃癌细胞株侵袭和生长的影响
Authors Zhang SS, Wu LH, Liu Q, Chen KS, Zhang XF
Published Date January 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 223—231
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S74075
Received 15 September 2014, Accepted 24 November 2014, Published 20 January 2015
Background: Gastric
adenocarcinoma is a predominant disease with latent attribute, high malignancy,
and poor prognosis in People’s Republic of China. Gastric cancer is the most
common malignant tumor of the digestive tract. It has been suggested that
abnormal expression of NEDD9 was associated with stage progression and
metabolism of carcinomas. Some authors demonstrated that both messenger RNA
(mRNA) and protein of NEDD9 were highly expressed in gastric cancer, and paired
paracancerous atypical hyperplasia tissues were correlated with lymph node
metastasis, tumor depth, and tumor-lymph node-metastasis (TNM) staging. In this
study, we found that NEDD9 small interfering RNA (siRNA) can induce apoptosis
and suppress proliferation, migration, and invasion of BGC823 cell lines. These
findings suggested that NEDD9 siRNA might serve as a tumor suppressor by
targeting NEDD9 in gastric cancer cell. It has been suggested that abnormal
expression of NEDD9 was associated with carcinogenesis, and in the first part
of the study, we found that NEDD9 was highly expressed in gastric cancer
tissues; and it too was correlated with lymph node metastasis, tumor depth, and
TNM staging. In this project, experiments were carried out to silence NEDD9 in
BGC823 cell lines using NEDD9 siRNA, and the biological activity of BGC823 cells
was observed after RNA interference.
Methods: The target analysis of
NEDD9 siRNA was forecast using online tools. In order to determine a more
efficient NEDD9 siRNA, three pairs of NEDD9 siRNA primer were designed,
synthesized, and then transfected into BGC823 cells. NEDD9-2 siRNA was finally
adopted by detecting the quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
(qRT-PCR). Cells were collected for detecting mRNA by qRT-PCR or protein by
western blot analysis. Cell apoptosis was detected using flow cytometry, and
the transwell invasion system was used for cell migration and invasion assays.
The effect of NEDD9 siRNA in silencing the target gene in BGC823 cells was then
assessed. Also, the impact of NEDD9-2 siRNA on cell proliferation, apoptosis,
migration, and invasion were detected in BGC823 cell lines.
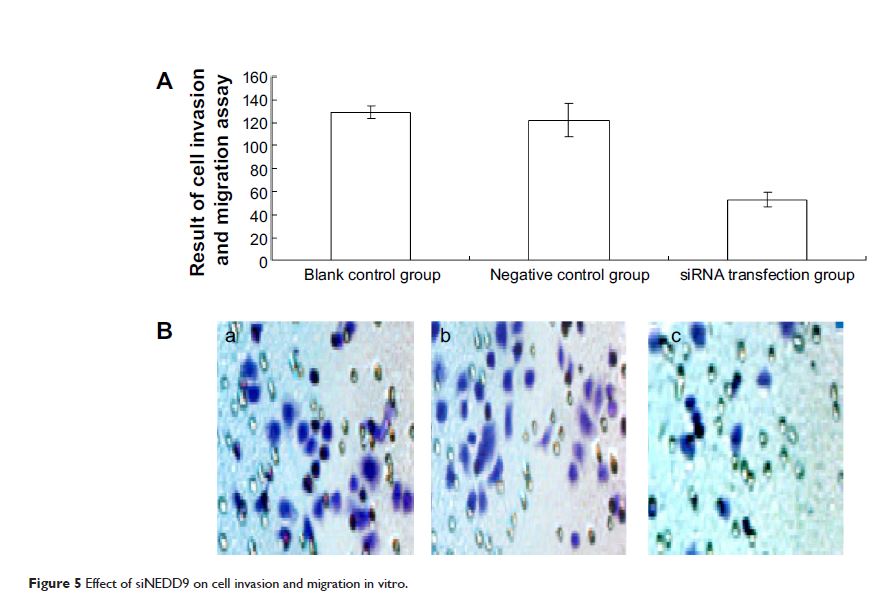
Results: The relative quantity
of expression of mRNA and protein showed a decrease in all cells transfected
with siNEDD9-2 at different concentrations. The cell proliferation inhibition
assay showed that the inhibition rate was significantly increased in all
transfected cells compared with control groups. Cell apoptosis assay showed
that the number of living cells were significantly reduced compared with
control groups, and cell migration and invasion assay showed that siNEDD9 could
inhibit BGC823 cell migration and invasion in vitro.
Conclusion: NEDD9 siRNA could
inhibit expression of NEDD9 and induce apoptosis, suppress proliferation,
migration, and invasion of BGC823 cells, acting as a tumor suppressor in
carcinogenesis of gastric cancer. These findings suggested that NEDD9 siRNA
plays an important role in the proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion of BGC823
cells.
Keywords: NEDD9 siRNA,
apoptosis