100205
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
使用 TAT-LHRH 耦联低分子量壳聚糖作为特异性针对肝脏癌细胞的基因载体
Authors Liu LX, Dong X, Zhu DW, Song LP, Zhang HL, Leng XG
Published Date June 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 2879—2889
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S61392
Received 27 January 2014, Accepted 12 April 2014, Published 10 June 2014
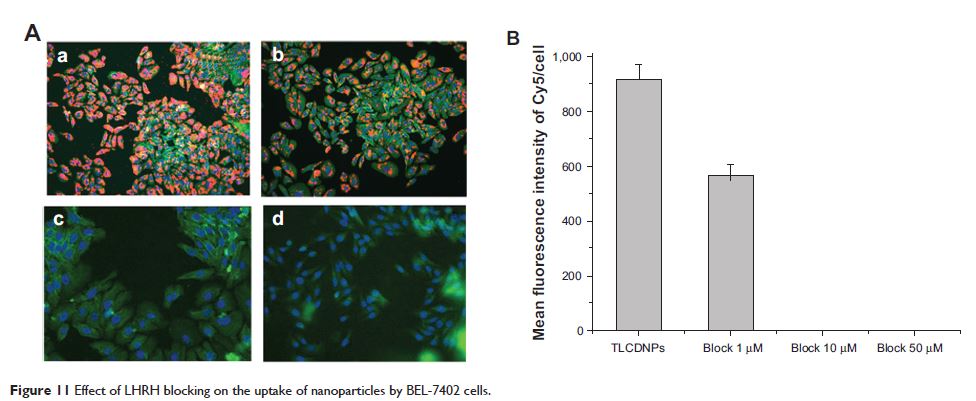
Abstract: To develop a chitosan-based nonviral gene carrier capable of delivering genes specifically into hepatoma cells, a bifunctional peptide composed of the TAT (transactivator of transcription) peptide and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) was conjugated with low molecular weight chitosan, resulting in a TAT-LHRH-chitosan conjugate (TLC). TLC/DNA nanoparticles (TLCDNPs) were characterized by agarose gel retardation, atomic force microscopy, and dynamic light scattering analysis. In vitro targeting specificity and transfection efficiency were analyzed with a GE IN Cell Analyzer 2000 High-Content Cellular Analysis System. The results demonstrated that TLC had stronger DNA condensing power than unmodified chitosan, and that TLCDNPs were of roughly round shape with average diameter of 70–85 nm and zeta potential of +30 mV and were relatively stable in solution. The in vitro study demonstrated TLC was highly selective for hepatoma cells and essentially nontoxic.
Keywords: nanoparticles, cancer treatment, gene therapy, hepatoma, targeted gene delivery
Keywords: nanoparticles, cancer treatment, gene therapy, hepatoma, targeted gene delivery
Download Article[PDF]