100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

老年患者急性心肌梗死和医院代谢综合症的医疗成本研究
Authors Fan GQ, Fu KL, Jin CW, Wang XZ, Han L, Wang H, Zhong M, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Wang ZH
Published Date January 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 329—337
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S70372
Received 1 July 2014, Accepted 7 August 2014, Published 23 January 2015
Background: Older
patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) usually have a poor prognosis,
but whether this poor prognosis leads to high hospital costs remains unclear.
This study investigated the clinical outcomes of and costs incurred by older
patients with AMI and metabolic syndrome (MS) in hospital.
Methods and results: Patients
with AMI seen at Qilu Hospital of Shandong University between January
2011 and May 2013 were separated into four groups: young non-MS
patients (n=282), older non-MS patients (n=324), young MS patients (n=217), and
older MS patients (n=174). We found that advanced age was significantly
associated with worse clinical outcomes, and that the clinical outcomes in
patients with AMI and MS are also worsened. At the same cost (RMB¥10,000),
older patients with and without MS had a markedly increased number of
cardiovascular incidences compared with younger patients without MS. In a
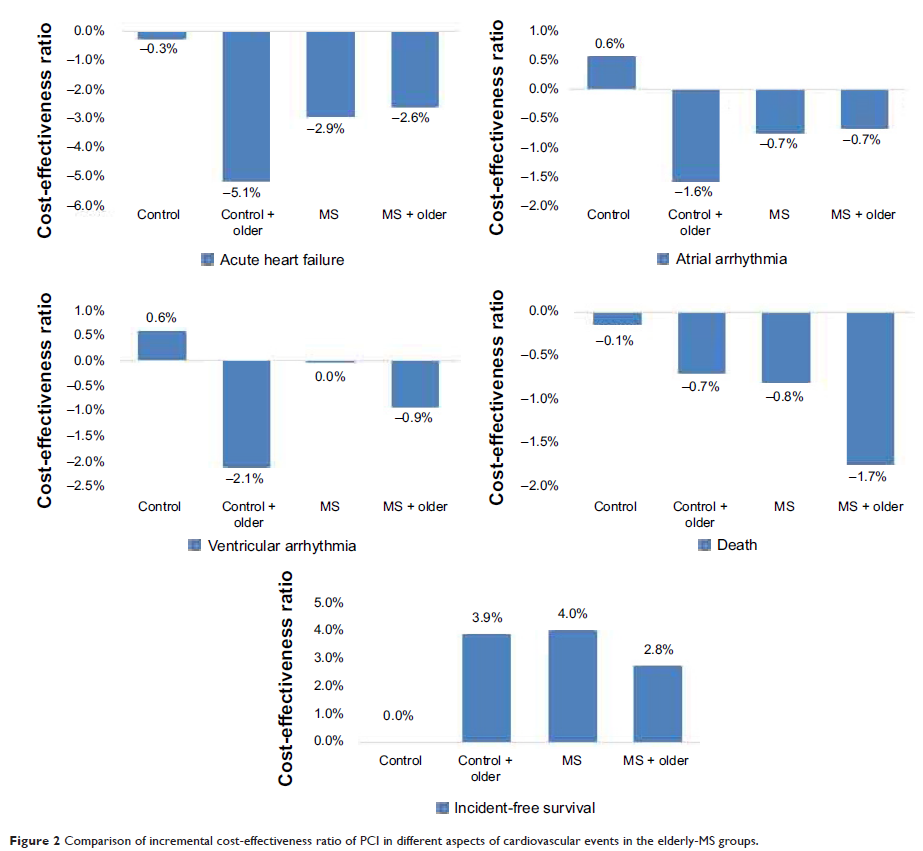
comparison of the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of percutaneous
coronary intervention, older patients without MS had a lower ICER for
cardiovascular incidences and a higher ICER for cardiac event-free survival
rate when compared with young patients without MS, but a lower ICER for cardiovascular
incidences and a higher ICER for cardiac event-free survival rate when compared
with older MS patients.
Conclusion: Older AMI patients
have poor clinical outcomes and their treatment is not cost-effective; however,
the results are worse in patients with AMI and MS. Percutaneous coronary
intervention is a cost-effective therapy in older patients with AMI, but its
cost-effectiveness decreases in patients with AMI and MS.
Keywords: metabolic syndrome,
aging, vascular, acute myocardial infarction, cost-effectiveness