100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

具有提高的稳定性和止血效率的含阳离子直链淀粉衍生物的凝血酶的纳米络合作用
Authors Zhuang B, Li Z, Pang J, Li W, Huang P, Wang J, Zhou Y, Lin Q, Zhou Q, Ye X, Ye H, Liu Y, Zhang LM, Chen R
Published Date January 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 939—947
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S72553
Received 11 August 2014, Accepted 25 October 2014, Published 29 January 2015
Abstract: As a
topical hemostatic agent, thrombin has wide application for many surgical
treatments. However, native thrombin always suffers from its physical and
chemical instabilities. In this work, a nanocomplexation strategy was developed
for modifying the stability and hemostatic efficacy of thrombin, in which a
water-soluble cationic amylose derivative containing poly(l-lysine) dendrons
was prepared by a click reaction and then used to complex thrombin in an
aqueous system. For resultant thrombin nanocomplexes, their morphology and
particle size distribution were investigated. Their stabilities were studied in
terms of activity retention percentages under different storage time, pH
values, and illumination time. In addition, their ability to achieve in vitro
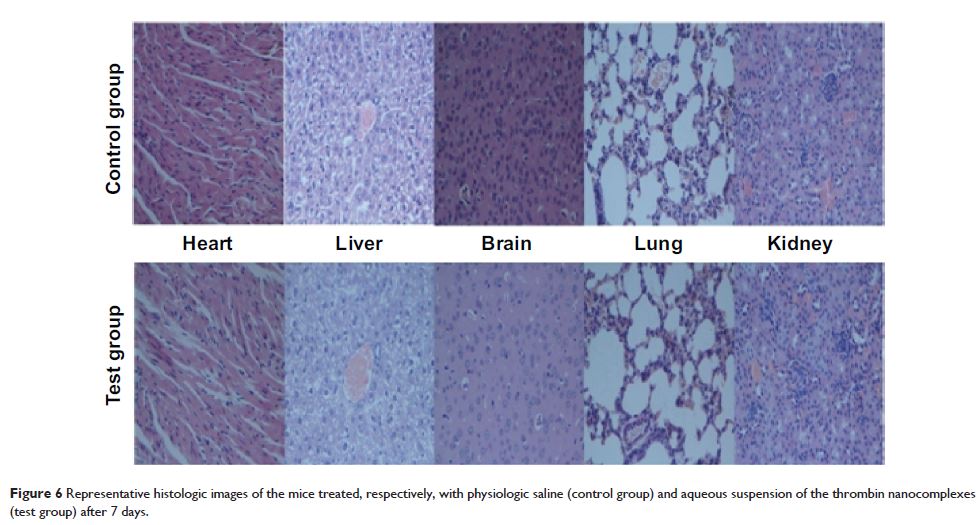
fibrinogen and blood coagulation were evaluated. Via a rat hepatic hemorrhage
model and a rat iliac artery hemorrhage model, these thrombin nanocomplexes
were confirmed to have good tissue biocompatibility and in vivo hemostatic
effectiveness.
Keywords: thrombin,
nanoparticles, amylose derivative, complexation, stability, hemostatic activity