100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用量子点和色层分析试纸对 C 反应蛋白进行快速定量检测
Authors Cheng X, Pu X, Jun P, Zhu X, Zhu D, Chen M
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 5619—5626
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S74751
Received 22 September 2014, Accepted 1 November 2014, Published 2 December 2014
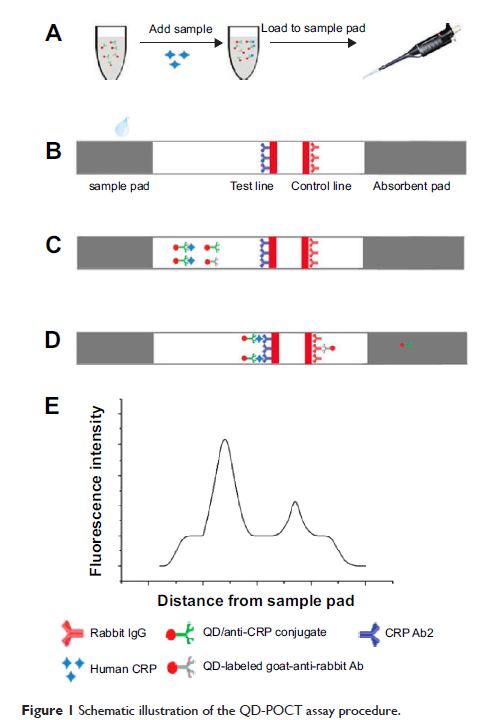
Background: Rapid
immunochromatographic tests can detect disease markers in 10–15 minutes, which
facilitates clinical diagnosis and treatment programs. However, most
immunochromatographic tests employ gold nanoparticles as reporters, and these
have only moderate sensitivity and act as qualitative methods for analyzing
high biomarker concentrations.
Methods: In this study, we
introduce quantum dots (QDs) as fluorescent probes and immunochromatographic
strips to develop quantitative fluorescence point-of-care tests (QF-POCT) to
analyze C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Goat anti-rabbit IgG and rabbit IgG
were used as control antibodies, and mouse monoclonal CRP antibody pairs were
used for disease marker detection. One monoclonal CRP antibody was conjugated
with QDs and served as a signal antibody, and the other monoclonal CRP antibody
was dispensed onto the nitrocellulose membrane and served as a capturing
antibody. In the presence of CRP, the fluorescence intensity of the monoclonal
antibody-CRP-monoclonal antibody sandwich complex captured on the
nitrocellulose membrane was determined using the fluorescence strip reader.
Results: QF-POCT assays could
quantitatively analyze the concentration of CRP in 15 minutes had a detection
limit of 0.25 mg/L, and had a wide detection linearity range (0.5–300 mg/L).
The intra-assay and interassay coefficients of variation were 8.95% and 9.86%
at 0.5 mg/L, 6.47% and 8.66% at 10 mg/L, and 6.81% and 9.10% at 60 mg/L,
respectively. In a comparison between clinical samples, the results of this
QD-based assay of CRP levels were significantly correlated with those of an
Immulite 2000 assay (R =0.993, P <0.001).
Conclusion: Our results
demonstrated that the QD-based immunochromatographic test is a rapid,
sensitive, accurate, and quantitative method for the detection of disease
biomarkers.
Keywords: C-reactive protein,
immunochromatographic test, quantum dots, fluorescence point-of-care test