100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

以聚乙二醇金纳米粒子辅助的计算机断层扫描对动脉粥样硬化中巨噬细胞的无创检测
Authors Qin J, Peng C, Zhao B, Ye K, Yuan F, Peng Z, Yang X, Huang L, Jiang M, Zhao Q, Tang G, Lu X
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 5575—5590
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S72819
Received 17 August 2014, Accepted 27 September 2014, Published 2 December 2014
Abstract: Macrophages
are becoming increasingly significant in the progression of atherosclerosis
(AS). Molecular imaging of macrophages may improve the detection and
characterization of AS. In this study, dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles
(Au DENPs) with polyethylene glycol (PEG) and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FI)
coatings were designed, tested, and applied as contrast agents for the enhanced
computed tomography (CT) imaging of macrophages in atherosclerotic lesions.
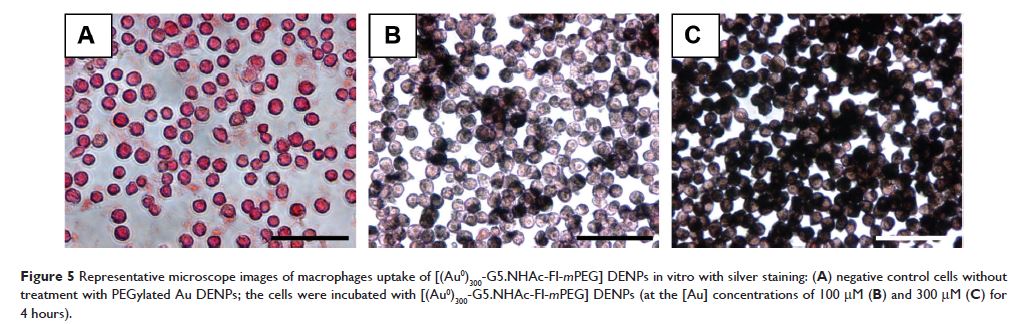
Cell counting kit-8 assay, fluorescence microscopy, silver staining, and
transmission electron microscopy revealed that the FI-functionalized Au DENPs
are noncytotoxic at high concentrations (3.0 µM) and can be efficiently
taken up by murine macrophages in vitro. These nanoparticles were administered
to apolipoprotein E knockout mice as AS models, which demonstrated that the
macrophage burden in atherosclerotic areas can be tracked noninvasively and
dynamically three-dimensionally in live animals using micro-CT. Our findings
suggest that the designed PEGylated gold nanoparticles are promising
biocompatible nanoprobes for the CT imaging of macrophages in atherosclerotic
lesions and will provide new insights into the pathophysiology of AS and other
concerned inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: atherosclerosis, CT,
in vivo imaging