100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

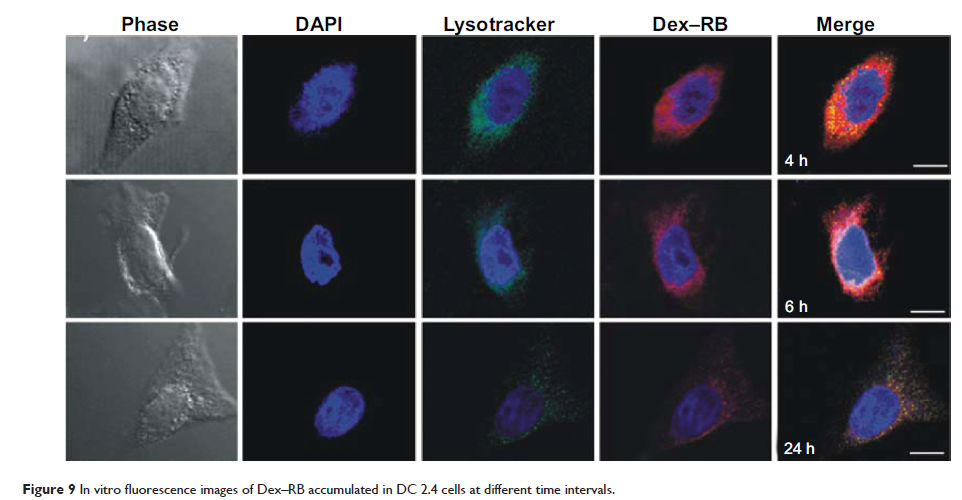
使用近红外发射可生物还原的右旋糖酐纳米凝胶进行前哨淋巴结荧光层析成像
Authors Li J, Jiang B, Lin C, Zhuang Z
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 5667—5682
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S70593
Received 3 July 2014, Accepted 3 September 2014, Published 4 December 2014
Abstract: Sentinel
lymph node (SLN) mapping is a critical procedure for SLN biopsy and its
diagnosis as tumor metastasis in clinical practice. However, SLN mapping agents
used in the clinic frequently cause side effects and complications in the
patients. Here, we report the development of a near-infrared (NIR) emitting
polymeric nanogel with hydrodynamic diameter of ~28 nm – which is the
optimal size for SLN uptake – for noninvasive fluorescence mapping of SLN in a
mouse. This polymeric nanogel was obtained by coupling Cy7, an NIR dye, to the
self-assembled nanogel from disulfide-linked dextran-deoxycholic acid conjugate
with the dextran of 10 kDa, denoted as Dex–Cy7. Fluorescence imaging
analysis showed that Dex–Cy7 nanogels had an enhanced photostability when
compared to Cy7 alone. After intradermal injection of Dex–Cy7 nanogel into the
front paw of a mouse, the nanogels were able to migrate into the mouse’s
axillary lymph node, exhibiting longer retention time and higher fluorescence
intensity in the node when compared to Cy7 alone. An immunohistofluorescence
assay revealed that the nanogels were localized in the central region of lymph
node and that the uptake was largely by the macrophages. In vitro and in
vivo toxicity results indicated that the dextran-based nanogels were of low
cytotoxicity at a polymer concentration up to 1,000 µg/mL and harmless to
normal liver and kidney organs in mice at an intravenous dose of
1.25 mg/kg. The results of this study suggest that NIR-emitting polymeric
nanogels based on bioreducible dextran-deoxycholic acid conjugates show high
potential as fluorescence nanoprobes for safe and noninvasive SLN mapping.
Keywords: nanogel, disulfide,
dextran, lymph node, tomographic imaging