100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

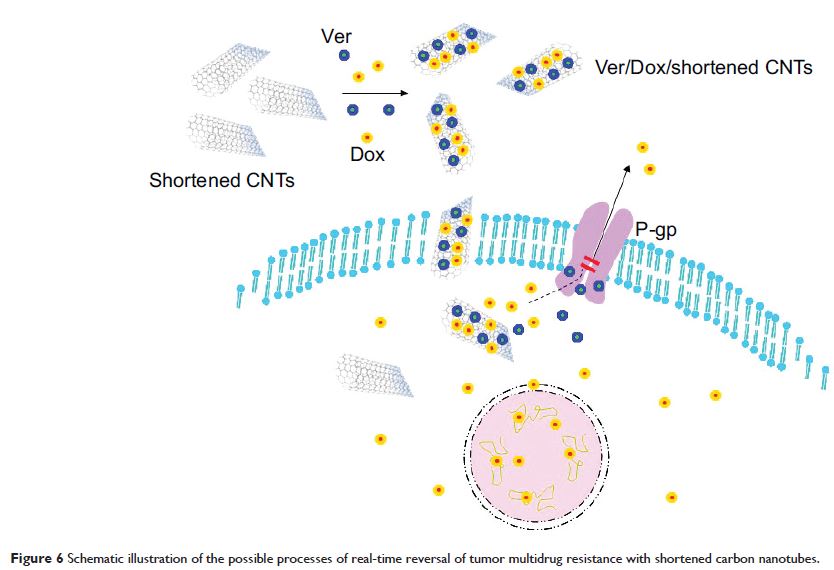
以缩短碳纳米管智能设计实时逆转肿瘤多药抗药
Authors Wu P, Li S, Zhang H
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 2431—2438
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S74962
Received 26 September 2014, Accepted 29 October 2014, Published 5 December 2014
Abstract: Multidrug
resistance (MDR) in tumors renders many currently available chemotherapeutic
drugs ineffective. Research in nanobiotechnology-based therapeutic alternatives
has provided innovative and promising strategies to overcome MDR. The aim of
this study was to investigate whether the new strategy of a co-loaded reversal
agent and chemotherapeutic drug with shortened carbon nanotubes (CNTs) would
show useful effects on the real-time reversal of tumor MDR. CNTs were cut and
purified via ultrasonication and oxidative acid treatment to optimize their
length for drug-delivery vehicles, then verapamil (Ver) and doxorubicin (Dox)
were co-loaded on shortened CNTs (denoted as Ver/Dox/shortened CNTs), which
acted as a drug delivery system. The multidrug resistant leukemia K562/A02
cells were treated with the denoted Ver/Dox/shortened CNTs. The real-time
reversal of tumor MDR were evaluated by flow cytometer,
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assays, acridine
orange/ethidium bromide staining, and Western blot analysis. In the same MDR
tumor cells the new strategy of a co-loaded reversal agent and chemotherapeutic
drug with CNTs could inhibit the function of P-glycoprotein in real-time by Ver
as reversal agent, significantly increase the uptake of Dox, enhance the
sensitivity of the MDR cancer cells to the chemotherapeutic agent, and induce
apoptosis. It was therefore concluded that a co-loaded reversal agent and
chemotherapeutic drug with shortened CNTs could have real-time reversal ability
of MDR in tumors, which could represent a promising approach in cancer therapy.
Keywords: multidrug resistance,
carbon nanotubes, drug delivery system, tumor