100763
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
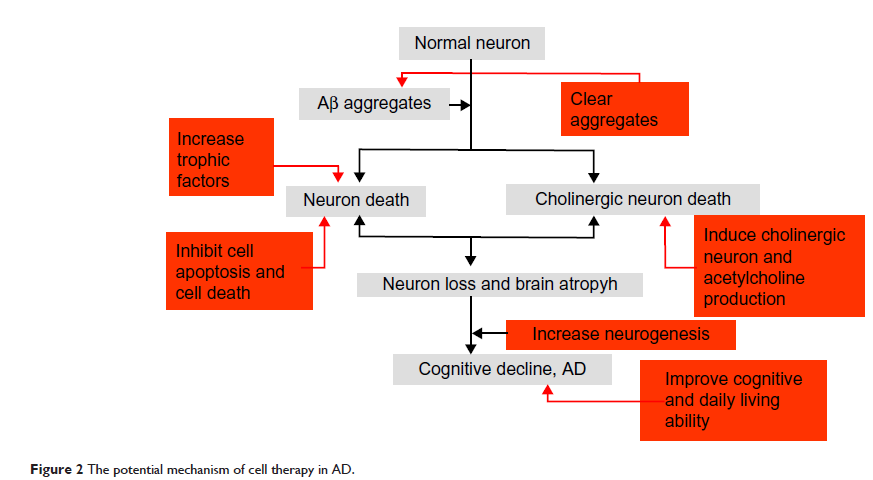
阿尔茨海默氏症临床神经复原进展
Authors Qiao L, Huang H, Muresanu DF
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2015:3 Pages 1—9
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/JN.S74143
Received 30 September 2014, Accepted 31 October 2014, Published 15 December 2014
Abstract: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most prevalent type of dementia, and
its neuropathology is characterized by the deposition of insoluble β-amyloid
peptides and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles and the loss of diverse
neurons. Although much is known about the neurobiology of AD, few treatments
are available to arrest or slow the illness. There is an urgent need for novel
therapeutic approaches for AD. We reviewed the recent improvements in the
neurorastorlogy strategies for AD, including medicine, bioengineering and
neuromodulation and clinical cell therapy. We emphasized that cell therapy may
be an promising treatment for AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease, neurorastorlogy, cell therapy, medicine
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease, neurorastorlogy, cell therapy, medicine
Download Article[PDF]